
Class
ES6에서 class 라는 문법이 추가 되었고, 기존의 prototype 기반으로 클래스를 만드는 것보다 명료하게 클래스를 만들 수 있게 되었습니다.
1. 클래스 정의
ES6에서 클래스는 특별한 함수입니다. 그렇기 때문에, 함수와 동일하게 클래스 선언(Class declarations)과 클래스 표현(Class expressions)으로 클래스를 만들 수 있습니다 ([자바스크립트] 함수(Function), 즉시실행함수(Immediately-invoked function expression) 참고)
클래스 선언(Class declarations)
class Polygon { constructor(height, width) { this.height = height; this.width = width; } }
클래스 선언은 함수 선언과 달리 호이스팅 되지 않습니다. ([자바스크립트] 유효범위(Scope)와 호이스팅(Hoisting) 참고)
var p = new Polygon(); // ReferenceError class Polygon {}

클래스 선언은 호이스팅 되지 않습니다.
클래스 표현(Class expressions)
익명 클래스와 기명 클래스를 만들 수 있습니다.
// unnamed var Polygon = class { constructor(height, width) { this.height = height; this.width = width; } }; // named var Polygon = class Polygon { constructor(height, width) { this.height = height; this.width = width; } };
클래스 표현(Class expressions) 또한 클래스 선언(Class declarations)와 같이 호이스팅(hoisting)이 되지 않습니다.
2. 메소드 정의
ES6의 class에서, 클래스의 몸통(body)는 {} 이며, class 메소드는 class의 {} 안에 정의해야 합니다.
Strict mode
클래스 몸통(body)는 strict mode로 실행됩니다. ([자바스크립트] 엄격 모드(strict mode) 참고)
생성자(Constructor)
생성자 메소드는 객체의 생성과 초기화를 하는 특별한 메소드입니다. 클래스에서 constructor 이름을 갖는 메소드는 하나여야 합니다.
var Polygon = class { constructor(height, width) { this.height = height; this.width = width; } constructor(height2, width2) { this.height = height2 * 2 ; this.width = width2 * 2; } };

constructor는 하나여야 합니다.
생성자 메소드에서 super 키워드를 통해 상위 클래스의 생성자 메소드를 호출 할 수 있습니다.
class Polygon { constructor(height, width) { this.height = height; this.width = width; } } class Square extends Polygon { constructor(length) { // length로 다각형의 넓이와 높이를 정의하기 위해 부모클래스의 생성자를 호출합니다. super(length, length); // Note: 파생 클래스에서, 'this'를 사용하기 전에는 반드시 super()를 // 호출하여야 합니다. 그렇지 않을 경우 참조에러가 발생합니다. this.name = 'Square'; } get area() { return this.height * this.width; } set area(value) { this.area = value; } } var test = new Square(4); console.log(test.area);
생성자 메소드에서 this를 사용하기 위해서 super 메소드를 먼저 호출해야 합니다.
set, get 함수의 선언법은 [자바스크립트] getter, setter 참고바랍니다.
프로토타입 메소드(Prototype methods)
class Polygon { constructor(height, width) { this.height = height; this.width = width; } get area() { return this.calcArea(); } calcArea() { return this.height * this.width; } } const square = new Polygon(10, 10); console.log(square.area);
ES6는 메소드 정의를 위한 더 짧은 구문이 도입되었습니다. 다음 코드가 주어지면,
var obj = { foo: function() {}, bar: function() {} };
ES6에서는 아래와 같이 줄일 수 있습니다.
var obj = { foo() {}, bar() {} };
정적 메소드(static methods)
static 메소드는 클래스의 인스턴스 (var a = new testFunc()) 필요없이 호출 가능합니다. 또한 클래스의 인스턴스에서 static 메소드를 호출 할 수 없습니다.
class Point { constructor(x, y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } static distance(a, b) { const dx = a.x - b.x; const dy = a.y - b.y; return Math.sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy); } } const p1 = new Point(5, 5); const p2 = new Point(10, 10); console.log(Point.distance(p1, p2)); var p3 = new Point(1, 1); p3.distance(p1, p2);
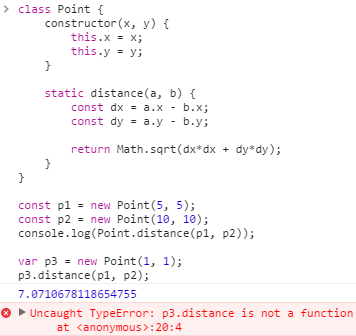
class의 static 메소드
인스턴스 없이 정상적으로 distance가 호출 되는 것과, 인스턴스를 통해 distance를 호출 할 때 TypeError가 발생하는 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
오토박싱(Autoboxing)
autoboxing이란?
일반 함수에서 this는 window 객체를 가르키게 됩니다. this가 window 객체 (global object)를 가르키는 이유는 autoboxing 덕분입니다.
non-strict 모드에서 ([자바스크립트] this의 정체 참고) this 값이 null 혹은 undefined 일 경우 window 객체(global object)로 자동으로 변환해 주는 것을 autoboxing이라고 합니다.
프로토타입 기반의 클래스에서 autoboxing
프로토타입 기반의 class의 경우
function Animal() { } Animal.prototype.speak = function(){ console.log(this); return this; } Animal.eat = function() { console.log(this); return this; } let obj = new Animal(); let speak = obj.speak; speak(); // global object let eat = Animal.eat; eat(); // global object

프로토타입 기반의 클래스의 autoboxing
autoboxing이 되어, 일반 함수를 호출하는 것처럼 메소드를 호출 한 경우 window 객체(global object)를 출력하는 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
ES6의 클래스 기반의 autoboxing
ES6의 class에서는 autoboxing이 되지 않습니다.
class Animal { speak() { console.log(this); return this; } static eat() { console.log(this); return this; } } let obj = new Animal(); let speak = obj.speak; speak(); // undefined obj.speak(); let eat = Animal.eat; eat(); // undefined Animal.eat();
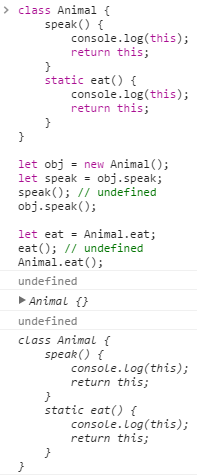
ES6의 class는 autoboxing이 안됨
autoboxing이 되지 않아, 일반 함수를 호출하는 것처럼 메소드를 호출 한 경우 undefined가 출력되는 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
그렇기 때문에 ES6의 클래스에서 메소드를 변수에 저장하여 사용할 경우, this에 유의해서 사용해야 합니다.
3. 클래스 상속(sub classing)
ES6의 클래스 상속
extends 키워드를 통하여 클래스를 상속 받아, 자식 클래스를 만들 수 있습니다.
class Animal { constructor(name) { this.name = name; } speak() { console.log(this.name + ' makes a noise.'); } } class Dog extends Animal { speak() { console.log(this.name + ' barks.'); } } var d = new Dog('Mitzie'); d.speak();
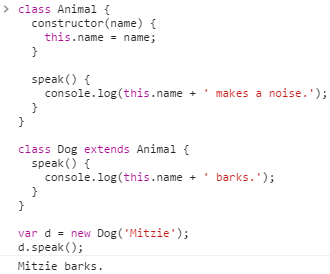
ES6의 클래스 상속
프로토타입 기반의 클래스 상속
프로토타입 기반의 클래스도 extends 키워드를 통해 상속 할 수 있습니다.
function Animal (name) { this.name = name; } Animal.prototype.speak = function () { console.log(this.name + ' makes a noise.'); } class Dog extends Animal { speak() { console.log(this.name + ' barks.'); } } var d = new Dog('Mitzie'); d.speak();

프로토타입 기반의 클래스 상속
일반 객체의 클래스 상속
일반 객체는 extends 키워드를 통해 상속할 수 없습니다. 상속하고 싶다면 Object.setPrototypeOf 메소드를 사용하여 상속해야 합니다.
var Animal = { speak() { console.log(this.name + ' makes a noise.'); } }; class Dog { constructor(name) { this.name = name; } speak() { console.log(this.name + ' barks.'); } } Object.setPrototypeOf(Dog.prototype, Animal); var d = new Dog('Mitzie'); d.speak();

일반 객체의 클래스 상속
4. Species
class MyArray extends Array { // 부모 Array 생성자로 종류 덮어쓰기 static get [Symbol.species]() { return Array; } } var a = new MyArray(1,2,3); var mapped = a.map(x => x * x); console.log(mapped instanceof MyArray); // false console.log(mapped instanceof Array); // true
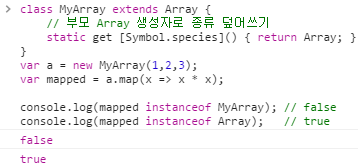
Symbol.species
Array를 상속받은 MyArray에서 Array의 default 생성자를 덮어 쓰고 싶을 경우, Symbol.species를 사용하면 됩니다. (get []의 문법은 [자바스크립트] getter, setter 참고 바랍니다.)
Symbol.species로 Array의 생성자를 가져오고, get [] 로 Array를 리턴함으로 부모 Array의 생성자를 덮어 쓸 수 있습니다.
5. super로 부모 클래스 호출하기
super 키워드를 홈하여 부모 클래스의 메소드를 호출 할 수 있습니다.
프로토타입 기반의 부모 클래스 메소드 호출
function Cat(name) { this.name = name; } Cat.prototype.speak = function () { console.log(this.name + ' makes a noise.'); }; function Lion(name) { // `super()` 호출 Cat.call(this, name); } // `Cat` 클래스 상속 Lion.prototype = new Cat(); Lion.prototype.constructor = Lion; // `speak()` 메서드 오버라이드 Lion.prototype.speak = function () { Cat.prototype.speak.call(this); console.log(this.name + ' roars.'); }; var lion = new Lion("BIG"); lion.speak();

프로토타입 기반의 부모 클래스 메소드 호출
프로토타입 기반의 클래스에서 부모 클래스의 메소드를 호출하기 위해서 call과 같은 함수를 사용해야 합니다. ([자바스크립트] API - call, apply 함수 참고)
ES6 클래스 기반의 부모 클래스 메소드 호출
class Cat { constructor(name) { this.name = name; } speak() { console.log(this.name + ' makes a noise.'); } } class Lion extends Cat { speak() { super.speak(); console.log(this.name + ' roars.'); } } var lion = new Lion("BIG"); lion.speak();
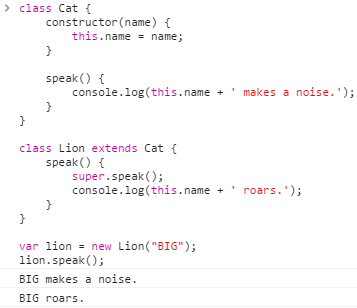
ES6 클래스 기반의 부모 클래스 메소드 호출
ES6 클래스는 super 메소드를 사용하여 부모 클래스의 메소드를 호출 할 수 있습니다.
출처: https://beomy.tistory.com/15 [beomy]
'WEB > JavaScript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Implementing Bubble Sort in Javascript (0) | 2021.06.11 |
|---|---|
| charAt 메서드 & charCodeAt 메서드 (0) | 2021.03.20 |
| ChatAt() vs ChatCodeAt() (0) | 2021.01.25 |
| JavaScript Type Casting (0) | 2021.01.25 |
| 자바스크립트 숫자의 자리수를 구하는 방법은? (0) | 2021.01.25 |