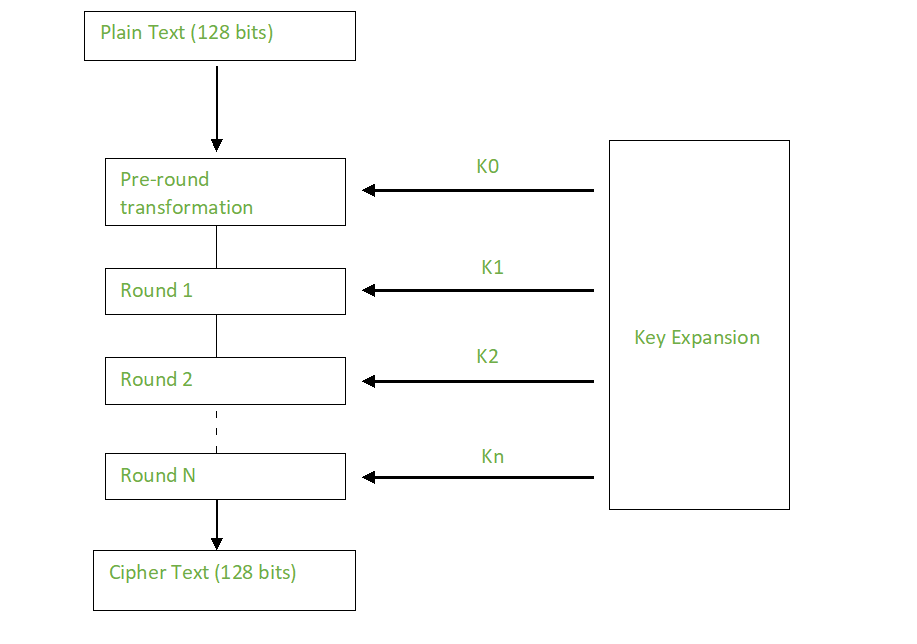
1. AES 암호 알고리즘(Advanced Encryption Standard)이란?
고급 암호화 표준(Advanced Encryption Standard)이라고 불리는 AES 암호 알고리즘은 DES를 대체한 암호 알고리즘이며 암호화와 복호화 과정에서 동일한 키를 사용하는 대칭 키 알고리즘이다.
DES에 비해서 키 사이즈가 자유롭다. 즉, 가변 길이의 블록과 가변 길이의 키 사용이 가능하다.(128bit, 192bit, 256bit)
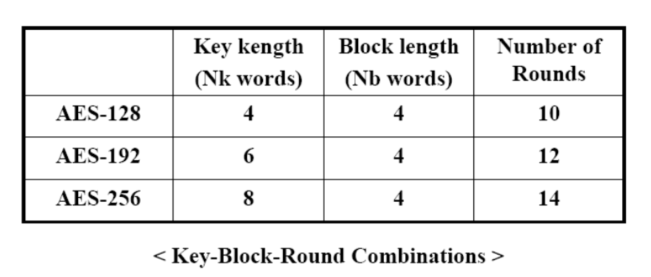
또한 속도와 코드 효율성 면에서 효율적이다.(즉, 디자인을 간단하게 하였다는 것이다.)
그리고 DES와 차이점은 페이스텔 구조가 아닌 SPN 구조를 이용한다.
SPN 구조
SPN은 Substitution - Permutation Network의 약자로
말 그대로 Substitution Layer와 Permuation Layer를 이용하여 Confusion과 Diffusion을 만족시켜주는 암호다.
아래 그림은 SPN 구조를 나타내고 있다.
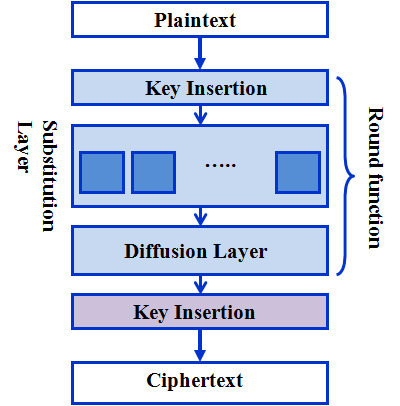
장점은 Feistel 구조와 반대로 병렬연산이 가능하고
단점은 복호화시 별도의 복호화 모듈을 구현해줘야 한다는 것이다.
SPN 구조 :: http://reinliebe.tistory.com/76
Feistel 구조와 SPN 구조의 차이
Feistel 구조는 암복호화 과정에서 역함수가 필요 없다는 장점이 있지만 구현시 스왑(Swap)단계 때문에 연산량이 많이 소요 되며 암호에 사용되는 라운드 함수를 안전하게 설계해야 한다는 단점이 있다.
대표적인 암호로는 DES가 있으며 Single DES는 안전성 문제로 현재 사용하고 있지 않다.
SPN 구조는 암복호화 과정에서 역함수가 필요하도록 설계되어야 한다는 단점이 있지만 중간에 비트의 이동없이 한번에 암복호화가 가능하기 때문에 페스탈 구조에 비해 효율적으로 설계할 수 있다. 대표적인 암호로는 AES가 있으며 AES는 현재 널리 상용되고 있다.
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EB%B8%94%EB%A1%9D_%EC%95%94%ED%98%B8
2. AES 암호 알고리즘 용어 설명
Cipher Key
Round Key들을 생성하기 위해 Key Expansion Routine에 의해 사용되어지는 암호키이다.
Key Expansion (= Key Schedule)
Cipher Key로부터 Round Key들을 생성하기 위해 사용되는 Routine이다.
Word
4 bytes의 배열이나 또는 한 entity로서 다뤄지는 32bits의 한 Group이다.
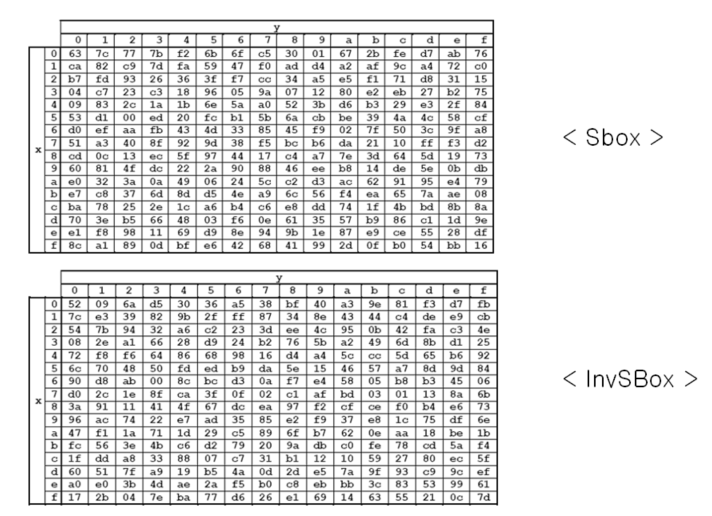
S-Box
Byte 값의 대체를 수행하기 위해 Key Expansion Routine과 여러 SubBytes 변환에서 사용되는 비선형 대칭표다.
파라미터
Nb : State를 구성하는 열의 수(Nb = 4)
Nk : 암호키를 구성하는 32-bit words의 수(Nk = 4, 6, 8)
Nr : 라운드의 수(Nr = 10, 12, 14)
State
암호화 중간 단계의 결과물로서 (4, Nb)의 이차원 행렬로 표현된다.(Nb는 128, 192, 256에서 4로 고정이다.)

3. AES 암호화 과정
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
for (round = 1; round<Nr; round++)
{
SubBytes();
ShiftRows();
MixColumns();
AddRoundKey(round);
}
SubBytes();
ShiftRows();
AddRoundKey(Nr);
// This source code Copyright belongs to Crocus
// If you want to see more? click here >>
|
Crocus |
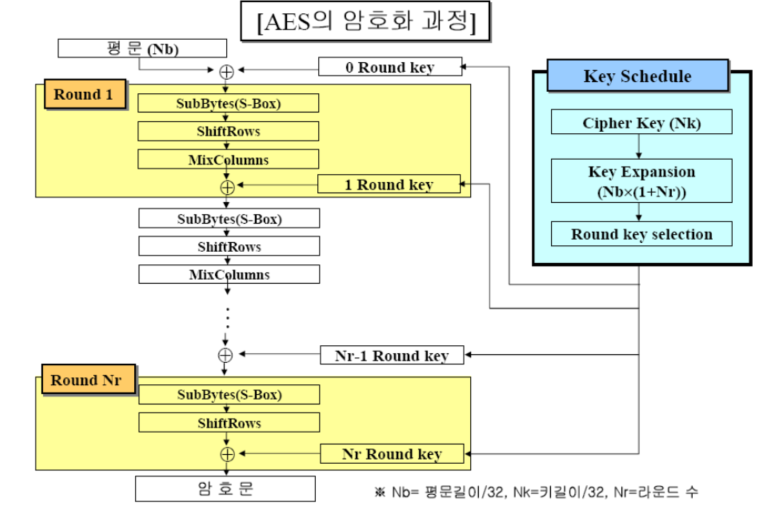
AES 암호화 과정은 위의 과정이 전부이다.
즉, round를 거쳐 암호화가 이루어지는데 좀더 자세한 내용은 위의 그림을 참조하면 된다.
여기서 이 코드를 보면 마지막 Nr 단계에서는 MixColumns를 실행하지 않는데
AES 암호 알고리즘에서 마지막 라운드에서는 MixColumn 단계가 없다는 것을 의미한다.
즉, 키가 128비트 였다면 Nr은 10이 되고 마지막 라운드인 10단계에서는 MixColumn이 없다는 것이다.
라운드 과정을 좀 더 자세히 살펴보자.
1. SubBytes 과정
바로 예를 들어 설명해보려 한다.
예를 들어 128 비트 입력이 16진수로 32 30 31 32 31 30 36 30 30 32 4B 4B 57 4B 4B 57와 같으면 이것의 state 상태는 다음과 같다.
(이는 2012106002kkwkkw를 키로 두었을 때 16진수로 변환한 값이다.)
",="" sans-serif;font-size:13px"="" style="border: none; border-collapse: collapse;">
32
31
30
57
30
30
32
4B
31
36
4B
4B
32
30
4B
57
<AES 상태의 예>
이때 1바이트 값이 9a였다면 S-Box에 의해 b8로 변한다는 것이다.
여기서 4B는 B3으로 치환된다.

2. ShiftRows 과정
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
void ShiftRows()
{
unsigned char temp;
// Rotate first row 1 columns to left
temp = state[1][0];
state[1][0] = state[1][1];
state[1][1] = state[1][2];
state[1][2] = state[1][3];
state[1][3] = temp;
// Rotate second row 2 columns to left
temp = state[2][0];
state[2][0] = state[2][2];
state[2][2] = temp;
temp = state[2][1];
state[2][1] = state[2][3];
state[2][3] = temp;
// Rotate third row 3 columns to left
temp = state[3][0];
state[3][0] = state[3][3];
state[3][3] = state[3][2];
state[3][2] = state[3][1];
state[3][1] = temp;
}
// This source code Copyright belongs to Crocus
// If you want to see more? click here >>
|
Crocus |

상태 행렬의 행에 따른 왼쪽 방향의 Cyclic 회전을 수행한다.
첫 번째 행은 회전되지 않고,
두 번째 행은 1byte,
세 번째 행은 2bytes,
네 번째 행은 3bytes 만큼씩 왼쪽으로 Cyclic 회전한다.
3. MixColumns 과정
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
// xtime is a macro that finds the product of {02} and the argument to xtime modulo {1b}
#define xtime(x) ((x<<1) ^ (((x>>7) & 1) * 0x1b))
// MixColumns function mixes the columns of the state matrix
// The method used may look complicated, but it is easy if you know the underlying theory.
// Refer the documents specified above.
void MixColumns()
{
int i;
unsigned char Tmp, Tm, t;
for (i = 0; i<4; i++)
{
t = state[0][i];
Tmp = state[0][i] ^ state[1][i] ^ state[2][i] ^ state[3][i];
Tm = state[0][i] ^ state[1][i]; Tm = xtime(Tm); state[0][i] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;
Tm = state[1][i] ^ state[2][i]; Tm = xtime(Tm); state[1][i] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;
Tm = state[2][i] ^ state[3][i]; Tm = xtime(Tm); state[2][i] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;
Tm = state[3][i] ^ t; Tm = xtime(Tm); state[3][i] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;
}
}
// This source code Copyright belongs to Crocus
// If you want to see more? click here >>
|
Crocus |
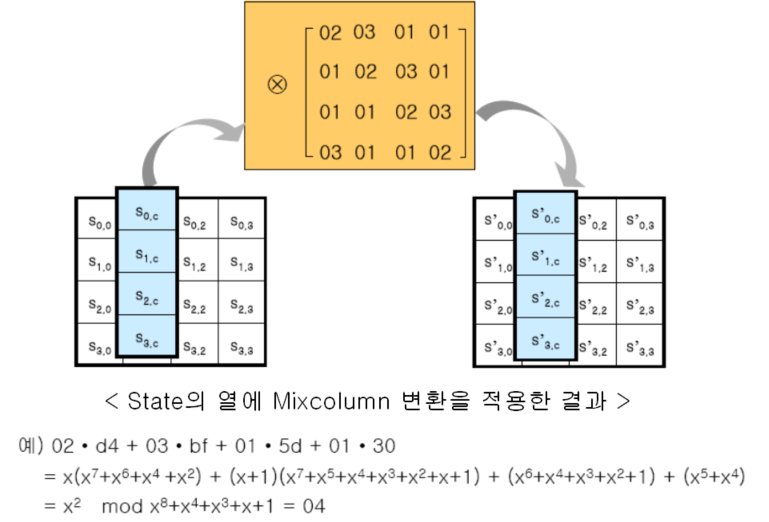

State의 각 Column에 대해서 아래와 같이 행렬 곱셈을 수행한다.
식에서 각 Symbol은 유한체 GF(28) 상의 요소이며 0 혹은 1의 계수를 갖는 7차 이하의 다항식으로 표현 가능하다.
그리고 요소간 곱셈은 기약 다항식, x^8+x^4+x^3+x+1을 법으로 하는 다항식 곱셈이다.
마지막 라운드는 MixColumn을 하지 않는다.
이 부분은 난해한 부분이므로 아 이런거구나 정도로 느끼면 될 듯합니다.
4. AddRoundKey 과정
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
// This function adds the round key to state.
// The round key is added to the state by an XOR function.
void AddRoundKey(int round)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i<4; i++)
for (j = 0; j<4; j++)
state[j][i] ^= RoundKey[round * Nb * 4 + i * Nb + j];
}
// This source code Copyright belongs to Crocus
// If you want to see more? click here >>
|
Crocus |
실제 encryption은 이 과정에서 수행되는데, state내의 각각의 byte들이 각 RoundKey와 XOR연산 되어진다.
RoundKey는 key expansion schedule에 따라 key로부터 유도되어진다.
4. AES 암호 알고리즘 예제 코드 및 실습
AES 암호화 소스코드
AES 복호화 소스코드
2012106002kkwkkw를 2, 16진수로 표현하면 아래와 같다.
2진수 표현
00110010 00110000 00110001 00110010 00110001 00110000 00110110 00110000 00110000 00110010 01001011 01001011 01010111 01001011 01001011 01010111
16진수 표현
32 30 31 32 31 30 36 30 30 32 4B 4B 57 4B 4B 57
이를 키로 이용하여 암호화를 해보고자 한다.
평문은 ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP를 이용한다.

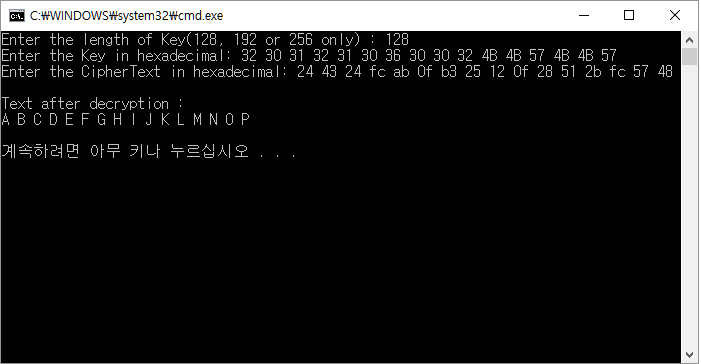
복호화시에도 2012106002kkwkkw를 키로 이용하여 32 30 31 32 31 30 36 30 30 32 4B 4B 57 4B 4B 57로 변환하고
암호화된 결과값을 넣으면 원본으로 복호화 할 수 있음을 알 수 있다.
'Cryptography' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Padding oracles and the decline of CBC-mode cipher suites (115) | 2024.03.08 |
|---|---|
| CBC-bit Flipping (54) | 2024.03.08 |
| Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) (31) | 2024.03.07 |
| 일부 변화가 있었던 ARIA 찾아서 조지기 (0) | 2024.03.04 |
| Double DES and Triple DES (0) | 2024.02.29 |